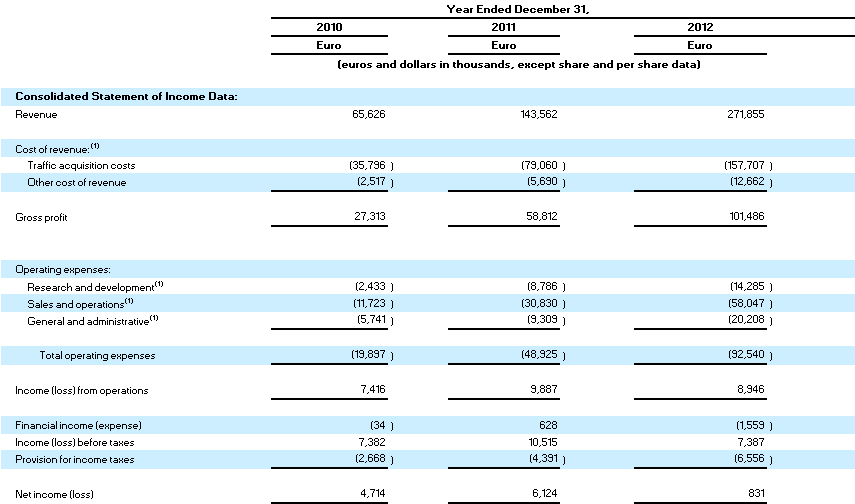
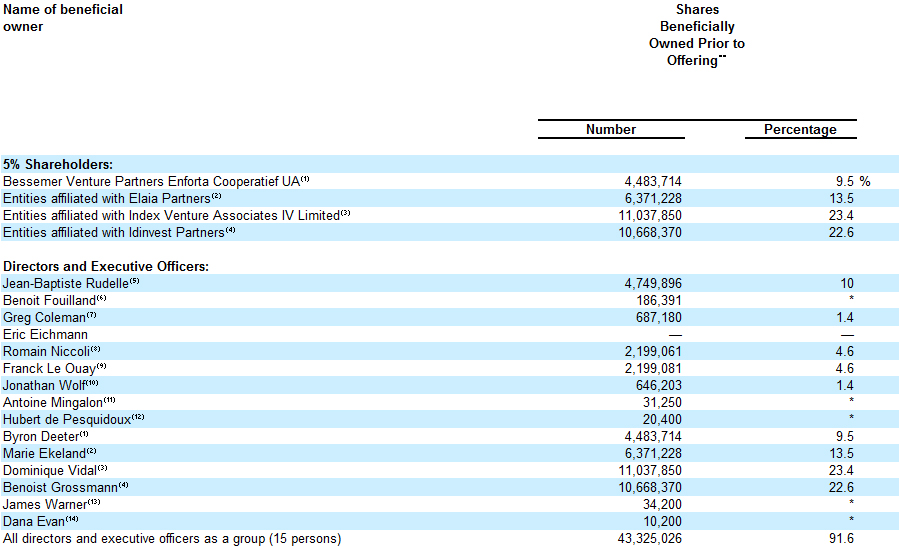
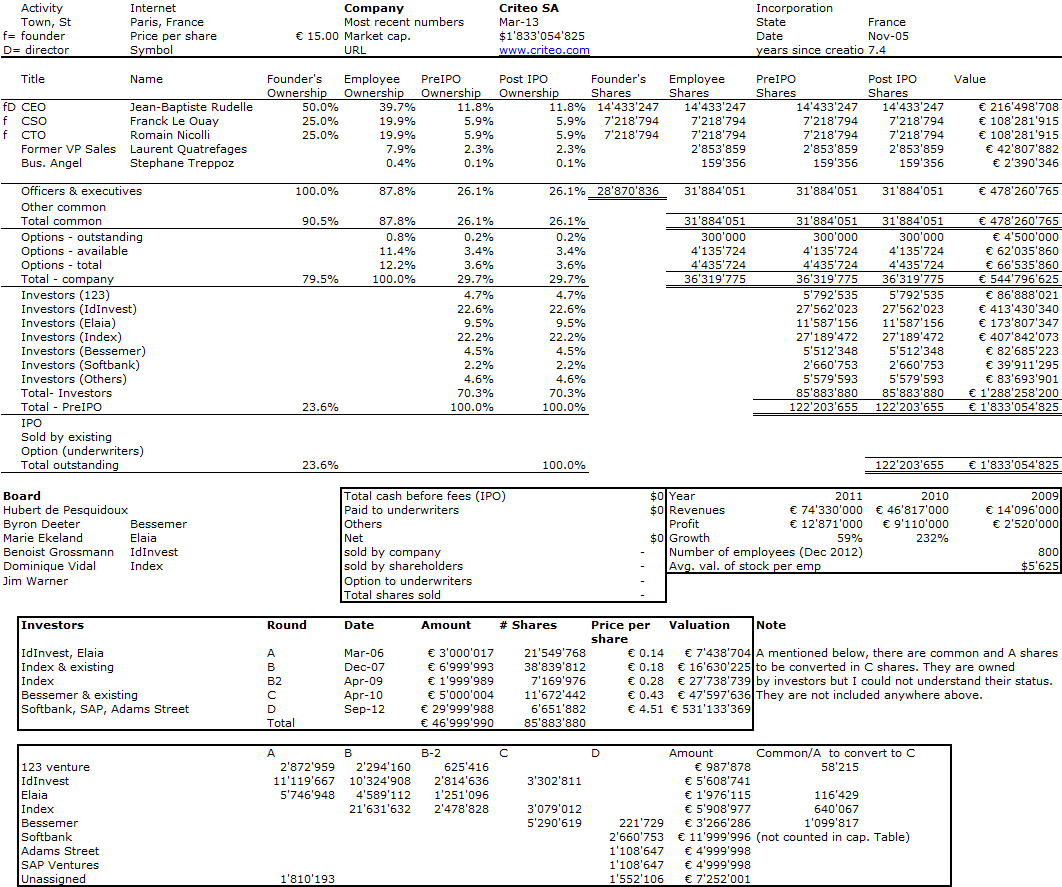
Movies may become a better way to communicate about start-ups & entrepreneurship than books or blogs. It’s something Neil Rimer had told me when I published my book. It is true there has been a number of new features in fiction (The Social Network, Jobs) and non-fiction (SomethingVentured) recently without a need to mention old stuff such as Triumph of the Nerds Silicon Valley Pirates and special events on television such as PBS.
Startup Kids belong to this new trend and it is an interesting (and fun) document. You may watch the trailer here and I will quote a few entrepreneurs thereafter. The document had been mentioned to me by colleagues (merci Corine ) who showed it to me, including the very good blog article of Sébastien Flury: The Startup Kids – a film that any wannabe founder should watch! (whom title I used, nice Sébastien 🙂 )
What’s entrepreneurship?

Drew Houston, Dropbox: “It’s like jumping out of a cliff and having to build your own parachute”

Kristian Segerstrale, Playfish: “An entrepreneur is a person who dares to have a dream that not many people have and even more important dares to chase it, put their money where their mouth is and their time and their career and dares to take the risk to going out there to realize that vision.”

Alexandre Ljung, SoundCloud (from Sweden and based in Berlin and San Francisco): “I did not have the typical entrepreneur background, […] but in hindsight I was very focused on projects so I was very entrepreneurial but not in a business sense.”
In European Founders at Work, his co-founder Eric Wahlforss states “I think we could have easily done this in one year faster if we would have been a little bit more bold and thinking a little bit more in terms of scale early on. We started out very small, had almost no money at all, and a very small team. I think we could have been bolder. […] and running with a bigger vision from the start.” And then “Do it.” It’s the best decision I’ve ever done in my whole life. […] And I was studying engineering as well, and I had one hundred classmates. And I know that almost zero of them actually went on to start a company, which is kind of crazy because I know a lot of them have good ideas. But none of them quite felt that they were able to pull it off.
Luck is an important topic in the movie
Segerstrale again: “Successful start-ups need a lot of things, they need a great idea, they need a great team, they need to be there at the right time, they need the right level of funding, and they need a lot of luck.”

Tim Draper, founder and investor, DFJ: “There is a lot of luck in the success of all the companies which have succeeded. You need a lot of luck, there were 25 search engines funded before Google was funded. There was Friendster and LinkedIn and MySpace and about 50 others before facebook became the big winner in that area.” [And it was the same with computer companies in the 80s!]

Finally do not miss Zach Klein (founder of Vimeo) in his beautiful wood cabin which reminds me of Thoreau’s Walden.