After my summer break, I received mails from friends and colleagues, all related somewhat to new (in fact old) trends in innovation. Thanks to Jean-Jacques, Andrea, Will and Martin :-). The four articles I read are:
– Les Misérables – Europe not only has a Euro crisis, it also has a growth crisis. That is because of its chronic failure to encourage ambitious entrepreneurs from the Economist (July 2012).
– Small is not beautiful from the Economist again (March 2012).
– In bid for start-ups, venture capitalists elbow their way into the spotlight from the International Herald tribune, (not freely available online).
– In Silicon Valley, Chieftains Hold Sway With Few Checks and Balances from the New York Times (July 2012)
The second one is probably the easiest to summarize and it is such an important message, that it needs to be hammered again: Innovation is not about large or small companies (SMEs), it is about fast growth (gazelles, start-ups). And let me add, it is also about a culture of trying and risk taking. “Rather than focusing on size, policymakers should look at growth.” […] “In a healthy economy, entrepreneurs with ideas can easily start companies, the best of which grow fast and the worst of which are quickly swept aside. Size doesn’t matter. Growth does.”
The first article is more complex to describe and I really liked only the first half. The second half explains that Europe struggles because of bad laws on bankruptcy, bad access to finance and bad labor laws. I am not sure these are the causes of our innovation crisis. I preferred the first part such as: “Europe’s culture is deeply inhospitable to entrepreneurs; wanting to grow a start-up into a behemoth is quite as countercultural as piercings and performance art.” […] “They will struggle to hire professional managers to help their firms grow, because European executives are extremely risk-averse. Their young firms will quickly find that established European companies tend not to like dealing with tiny ones.” And as a consequence, “the giants are all ageing”.
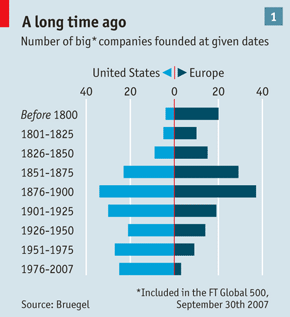
“Europe gave birth to just 12 new big companies between 1950 and 2007. America produced 52 in the same period (see chart above).” […] “Many aspiring entrepreneurs simply leave. There are about 50,000 Germans in Silicon Valley, and an estimated 500 start-ups in the San Francisco Bay area with French founders. One of the things they find there is a freedom to fail.” The answer is not simple, but there is hope: “There are schemes […] to get academics to hate business less, to expose schoolchildren to entrepreneurial notions.”
The last two articles are probably less important but give interesting new trends in Silicon Valley. One shows that the venture capitalists are becoming more visible (in order to court entrepreneurs) and mostly thanks to or because of new fund Andreessen Horowitz. But there is also debate (and I agree with the following comment): ‘‘I don’t quite understand the venture capital celebrity. We should be supporting actors. The entrepreneurs do the work and deserve the credit.’’ But Andreessen adds an interesting comment about the dynamics of venture capital: “Each year 15 deals account for 97 percent of all venture capital profits. To be successful, they would have to pursue those 15 companies. And they would do it by aggressively marketing their expertise to the reporters and bloggers who follow start-ups.” The final paper complains about the dangers of too much control to founders and managers vs. board or shareholders: “Since Google went public in 2004 in a way that maintained control for its founders, the leaders of Silicon Valley have been chary about shareholder voting rights.” […] “Directors are meant to act as a check on executives or at least add their expertise and advice to big decisions. In the Valley, however, the idea of the visionary chief executive dominates, and there may be little room for input from directors.” […] “So the new thing in Silicon Valley appears to be for public companies to be run as private ones without significant input from boards and shareholders. This leaves the wunderkinder of the Internet free to run their companies without interference. The question is whether this is merely a bubble in corporate governance or a trend that will spread to the rest of corporate America.”