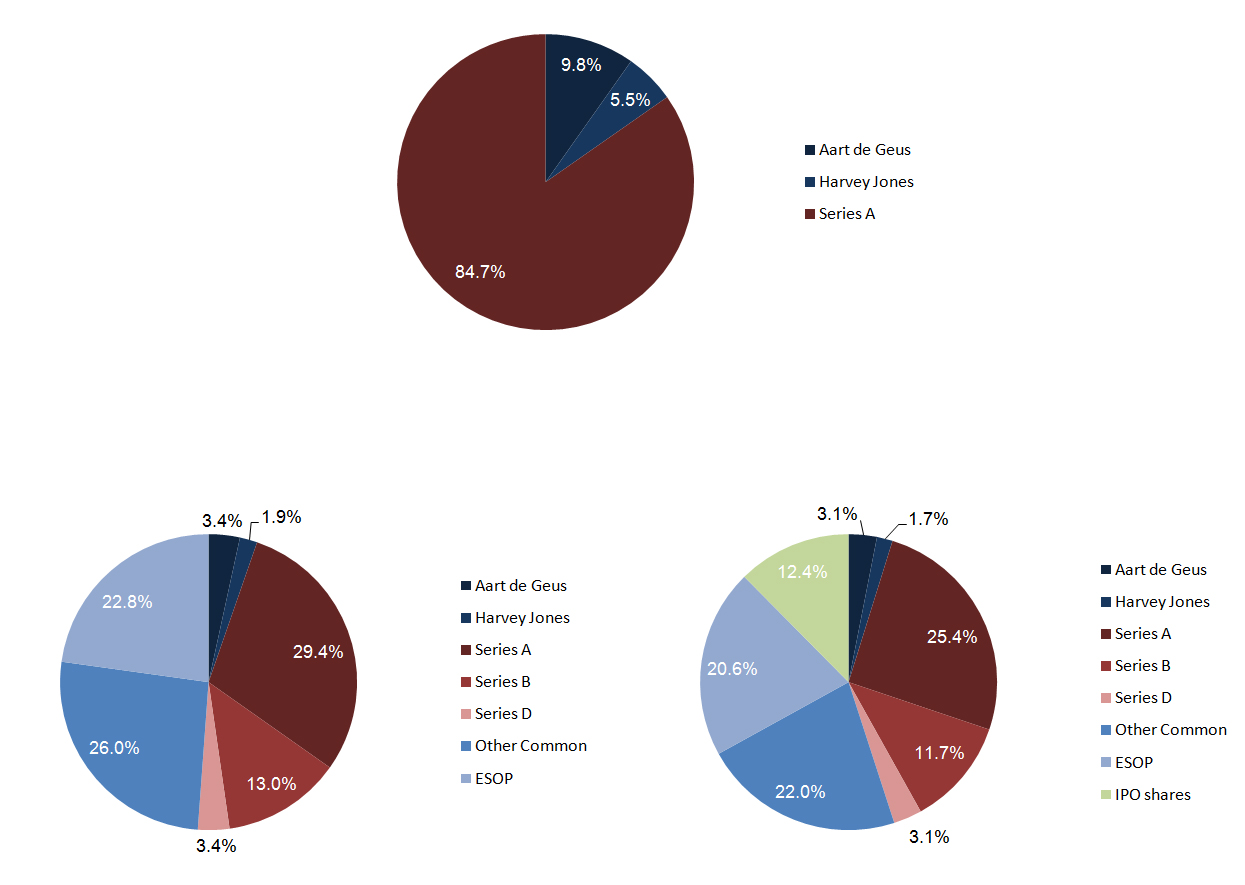
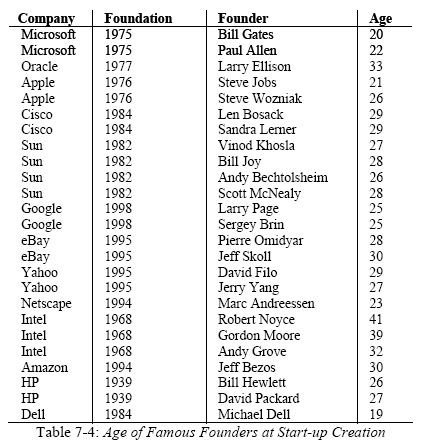
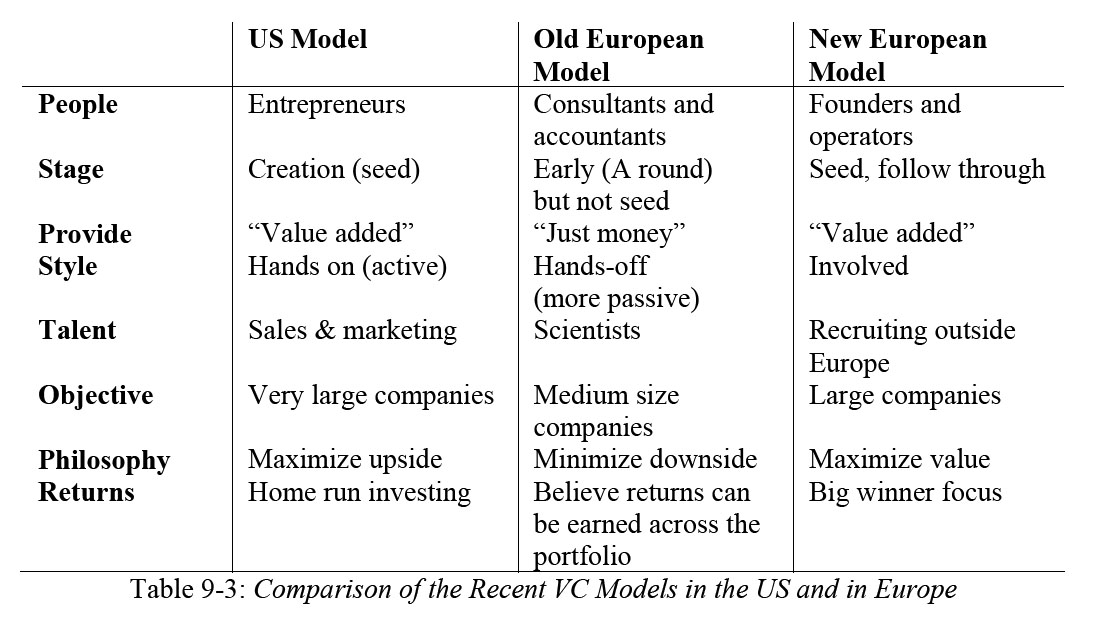
I seldom do it this way. I will not translate my French post about a personal analysis of the crisis and the American model. A crisis which is much more general than the financial and economic crisis. It is also a crisis of creativity, invention and innovation at least in Europe. So we look at the USA for a model and solutions. This creates tensions. Many of my friends and colleagues disagree with my fascination for the USA, which by the way, is limited to a very small number of things!
So I give a few directions including a previous post on the book by Lee Smolin, The Trouble with Physics. Go to French or if you do not, at least go and watch No One Knows About Persian Cats. Where’s the link? I think our crisis is about individuals and society, the inability of the university, of the school, of the family, of the society in general to let people express their dreams, their self-confidence, their creativity and their inventiveness. The pressure is so high that (self-)censorhsip and fraud prevail sometimes.
You may think I am out of my mind. So let me finish with the way I finished my book by quoting Wilhelm Reich from “Listen, Little Man”. A small essay by the number of pages, a big one in the impact it creates. “I want to tell you something, Little Man; you lost the meaning of what is best inside yourself. You strangled it. You kill it wherever you find it inside others, inside your children, inside your wife, inside your husband, inside your father and inside your mother. You are little and you want to remain little.” The Little Man, it’s you, it’s me. The Little Man is afraid, he only dreams of normality; it is inside all of us. We hide under the umbrella of authority and do not see our freedom anymore. Nothing comes without effort, without risk, without failure sometimes. “You look for happiness, but you prefer security, even at the cost of your spinal cord, even at the cost of your life”.
I am quite convinced that our crisis at least in Europe is about self-confidence, trust, creativity, inventiveness and innovation. It has not much to do with the technology, the economy and a lot to do with how individuals can grow in the society. If you followed me until now, thanks! Please, please, react!